IBM RPA vs. MetaGPT: AI Automation Titans Compared
AI-powered automation and development tools are transforming business operations across industries. IBM RPA vs. MetaGPT, and SmythOS each offer unique approaches to harnessing AI capabilities. This comparison explores how these platforms tackle enterprise automation, multi-agent collaboration, and AI integration.
We’ll examine their core features, security measures, and ease of use to help you determine which solution best fits your organization’s needs. Whether you’re a developer seeking powerful APIs, a business leader focused on scalability, or a non-technical user looking for accessible AI tools, this analysis provides insights to guide your decision-making process.
IBM RPA Overview
IBM RPA offers a robust platform for automating repetitive digital tasks across enterprise applications. This solution empowers businesses to create software robots, or bots, that interact with user interfaces just like human workers.
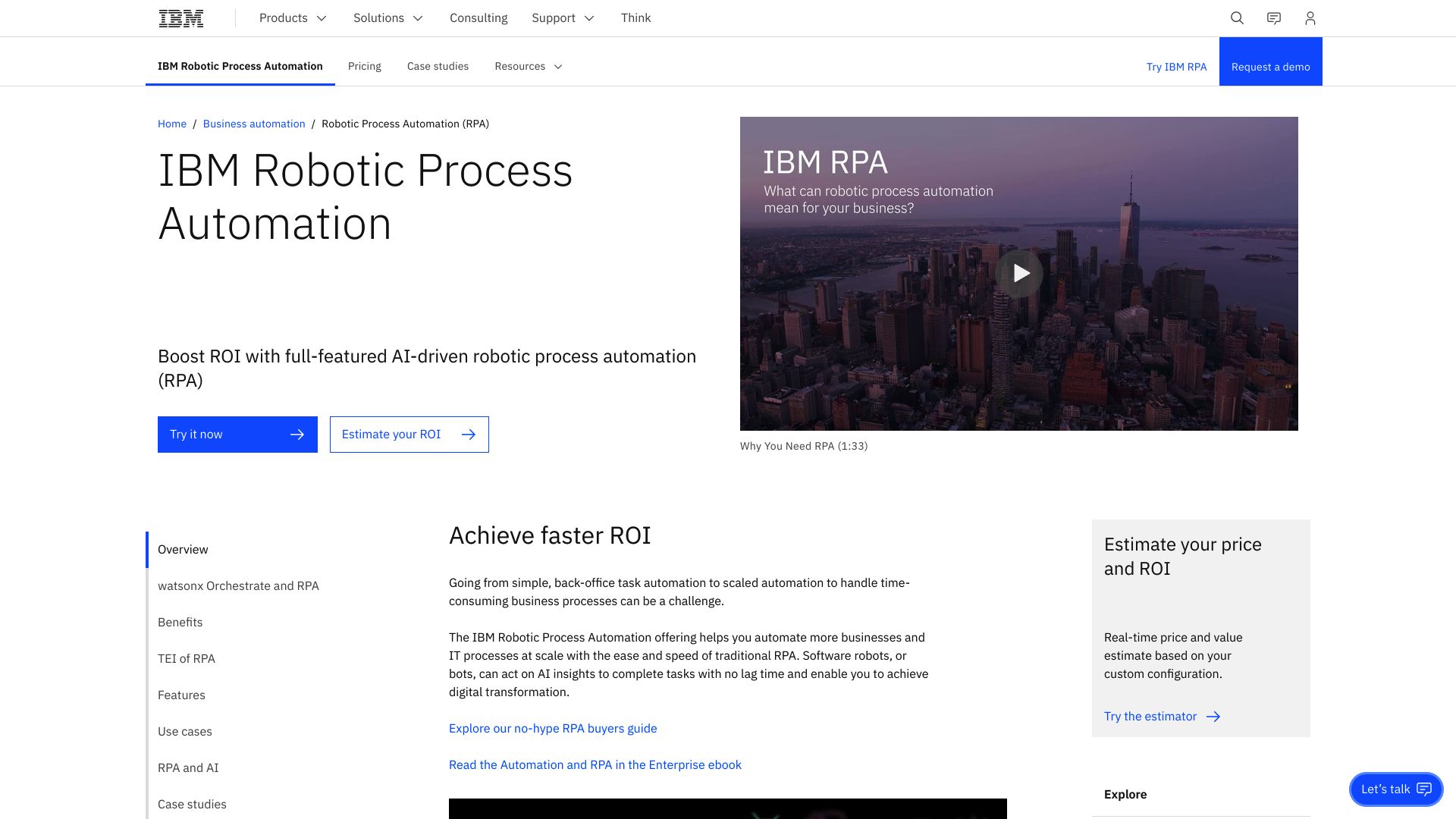

IBM RPA’s visual builder simplifies bot creation through drag-and-drop functionality, allowing users to design complex automation workflows without extensive coding knowledge. The platform supports both attended and unattended bots, enabling a flexible approach to task automation. Attended bots work alongside humans, enhancing productivity in customer-facing roles, while unattended bots operate autonomously, tackling back-office processes around the clock.
IBM RPA’s visual builder simplifies bot creation through drag-and-drop functionality, allowing users to design complex automation workflows without extensive coding knowledge.
Integration capabilities stand out as a key strength of IBM RPA. The platform seamlessly connects with a wide array of enterprise applications, including Office suites, SAP, Java-based systems, and web applications. This versatility allows organizations to implement end-to-end automation across diverse technological ecosystems.
IBM RPA addresses scalability concerns through distributed runtime environments and orchestration processes. This architecture enables businesses to deploy and manage large bot workforces efficiently, adapting to fluctuating workloads and organizational growth. However, users should note that complex integrations may require specialized knowledge, potentially increasing implementation time and costs.
Security and compliance features bolster IBM RPA’s appeal for enterprise users. The platform integrates with IBM OpenPages for governance, ensuring transparency and auditability in AI-driven processes. While this focus on enterprise-grade security is commendable, smaller organizations might find the associated complexity and potential overhead challenging to manage.
MetaGPT Overview
MetaGPT revolutionizes multi-agent collaboration by combining human Standardized Operating Procedures (SOPs) with advanced Large Language Models (LLMs). This open-source framework assigns distinct roles to AI agents, mirroring a traditional software company structure to enhance efficiency in complex tasks.

MetaGPT’s core philosophy, “Code = SOP(Team),” integrates established human practices into AI-driven processes. The platform breaks down tasks into manageable subtasks handled by specialized agents, ensuring each contributes its expertise to the overall project. This approach significantly reduces errors typically associated with multi-agent systems, such as cascading hallucinations or logic inconsistencies.
MetaGPT’s core philosophy, “Code = SOP(Team),” integrates established human practices into AI-driven processes. The platform breaks down tasks into manageable subtasks handled by specialized agents…
The framework generates comprehensive documentation throughout the development process, including requirement documents, design artifacts, flowcharts, and interface specifications. These intermediate outputs enhance the success rate of the final code and facilitate better human-AI interaction. MetaGPT’s ability to produce coherent, high-quality code while maintaining detailed documentation sets it apart in the AI development landscape.
MetaGPT’s unique selling point lies in its mimicry and improvement of human collaboration processes within an AI framework. By incorporating SOPs and specialized roles, it ensures AI agents work together efficiently, producing outputs that align with human standards and expectations. This approach improves multi-agent system performance and opens new possibilities for AI application in complex, real-world scenarios.
While MetaGPT offers powerful collaboration tools, users may face challenges in integrating it with existing systems or scaling for large-scale enterprise use. The open-source nature of the platform may require technical expertise for optimal utilization, potentially limiting its accessibility for non-technical users. As the field of AI agent builders evolves, MetaGPT’s focus on mimicking human workflows positions it as a significant player in advancing multi-agent AI systems.
Feature Comparison
IBM RPA and MetaGPT offer distinct approaches to automation and AI development, with notable differences in their core components and security features. IBM RPA provides a robust platform for automating repetitive digital tasks across enterprise applications, focusing on creating software robots that interact with user interfaces. In contrast, MetaGPT revolutionizes multi-agent collaboration by combining human Standardized Operating Procedures with advanced Large Language Models.
IBM RPA excels in enterprise-grade security and compliance, integrating with IBM OpenPages for governance and ensuring transparency in AI-driven processes. It offers strong data encryption and OAuth support, critical for handling sensitive enterprise data. MetaGPT, being open-source, may require additional security measures when implemented in enterprise environments. However, it compensates with its unique approach to AI agent collaboration, mimicking human team structures to enhance efficiency in complex tasks.
While both platforms support visual builders and no-code options, their implementations differ. IBM RPA’s visual builder is tailored for creating automation workflows, whereas MetaGPT’s approach focuses on generating comprehensive documentation and code through its multi-agent system. IBM RPA’s strength lies in its seamless integration with enterprise applications and scalable bot deployment, while MetaGPT shines in its ability to break down complex tasks into manageable subtasks handled by specialized AI agents, potentially offering more flexibility in tackling diverse AI development challenges.
Feature Comparison Table
| IBM RPA | MetaGPT | SmythOS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CORE FEATURES | |||
| AI Agents | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Visual Builder | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
| No-Code Options | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Memory & Context | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Autonomous Agents | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Explainability & Transparency | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Multimodal | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Problem-Solving Capabilities | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Multi-Agent Collaboration | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Work as Team | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| SECURITY | |||
| Constrained Alignment | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| OAuth | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| IP Control | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| COMPONENTS | |||
| Foundation AIs | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Huggingface AIs | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Zapier APIs | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Classifiers | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Data Lakes | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| DEPLOYMENT OPTIONS (EMBODIMENTS) | |||
| Deploy as Webhook | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Staging Domains | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Production Domains | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| API Authentication (OAuth + Key) | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Deploy as Site Chat | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Deploy as GPT | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| DATA LAKE SUPPORT | |||
| Hosted Vector Database | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Sitemap Crawler | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| YouTube Transcript Crawler | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| URL Crawler | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
Best Alternative to IBM RPA and MetaGPT
SmythOS emerges as the superior alternative to IBM RPA and MetaGPT, offering a comprehensive agentic AI automation platform that combines ease of use, an extensive feature set, and unlimited use cases. Our drag-and-drop interface revolutionizes AI agent creation, making it accessible to users of all skill levels while maintaining the power and flexibility needed for complex automation tasks.
SmythOS emerges as the superior alternative to IBM RPA and MetaGPT, offering a comprehensive agentic AI automation platform that combines ease of use, an extensive feature set, and unlimited use cases.
Unlike IBM RPA’s focus on repetitive task automation and MetaGPT’s emphasis on multi-agent collaboration, SmythOS provides a versatile ecosystem for developing and deploying AI agents across various applications. We offer a robust visual builder and no-code options, enabling rapid development and iteration of AI solutions without sacrificing advanced capabilities.
SmythOS excels in areas where IBM RPA and MetaGPT fall short. Our platform supports autonomous agents with memory and context, ensuring intelligent and persistent interactions. We provide multimodal capabilities, allowing agents to process and respond to various data types, including text, images, and more. Our problem-solving capabilities and multi-agent collaboration features surpass those of IBM RPA, while our user-friendly interface and deployment options outshine MetaGPT’s developer-centric approach.
Security and scalability are paramount in SmythOS. We offer enterprise-grade features like constrained alignment, data encryption, and OAuth support, addressing the needs of businesses handling sensitive information. Our platform scales effortlessly from small projects to large-scale deployments, accommodating growing demands without compromising performance.
By choosing SmythOS, users gain access to a cutting-edge AI operating system that democratizes AI development while providing the tools necessary for creating sophisticated, intelligent agents. Our platform’s versatility, from API integrations to deployment as chatbots or scheduled agents, ensures that SmythOS can adapt to any automation challenge, making it the ideal choice for businesses and developers seeking to harness the full potential of AI technology.
Conclusion
IBM RPA and MetaGPT offer powerful solutions for enterprise automation and AI development, each with unique strengths. IBM RPA excels in creating software robots for automating repetitive tasks across enterprise applications, with robust security features and seamless integration capabilities. MetaGPT stands out for its innovative approach to multi-agent collaboration, mimicking human team structures to enhance efficiency in complex AI tasks.
While both platforms have their merits, SmythOS emerges as the superior choice, combining the best of both worlds and offering additional advantages. Our drag-and-drop interface surpasses IBM RPA’s visual builder in simplicity and flexibility, allowing users to create sophisticated AI workflows without extensive coding knowledge. Unlike MetaGPT’s focus on software development, SmythOS provides a versatile platform for building and deploying AI agents across various domains and use cases.
SmythOS’s extensive integration ecosystem, supporting over 300,000 integrations, outshines both competitors in terms of connectivity and adaptability. Our platform’s ability to work with multiple AI models, including those from OpenAI, Anthropic, and Hugging Face, provides unparalleled flexibility. The ’Create Once, Deploy Anywhere’ approach allows for seamless deployment across various platforms, from chatbots to APIs, addressing diverse business needs more effectively than IBM RPA or MetaGPT.
For those looking to harness the full potential of AI in their operations, we invite you to explore our diverse range of AI-powered agent templates and get started with SmythOS. Experience the future of AI automation with our user-friendly platform, extensive integrations, and versatile deployment options. Unlock limitless AI integrations with SmythOS and revolutionize your workflow today.
Last updated:
Disclaimer: The information presented in this article is for general informational purposes only and is provided as is. While we strive to keep the content up-to-date and accurate, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability of the information contained in this article.
Any reliance you place on such information is strictly at your own risk. We reserve the right to make additions, deletions, or modifications to the contents of this article at any time without prior notice.
In no event will we be liable for any loss or damage including without limitation, indirect or consequential loss or damage, or any loss or damage whatsoever arising from loss of data, profits, or any other loss not specified herein arising out of, or in connection with, the use of this article.
Despite our best efforts, this article may contain oversights, errors, or omissions. If you notice any inaccuracies or have concerns about the content, please report them through our content feedback form. Your input helps us maintain the quality and reliability of our information.
