Fog Computing: Bridging Cloud and Edge
Connected devices are transforming data processing through fog computing, a decentralized infrastructure that brings cloud capabilities closer to IoT devices.
Autonomous vehicles now make split-second decisions locally, while smart factories optimize production in real-time on the factory floor. Fog computing achieves this by processing data near its source rather than in distant cloud servers.
Fog computing extends cloud capabilities to the network edge, reducing latency for time-sensitive applications. This local processing addresses key limitations of centralized cloud systems.
“Fog computing acts as a bridge between the cloud and IoT devices, enabling faster response times and more efficient use of network resources,” explains Dr. Maria Chen, Chief Technology Officer at EdgeTech Solutions.
This article examines fog computing’s core components, real-world applications, and benefits. For technology enthusiasts and business leaders alike, understanding fog computing is essential for leveraging edge computing effectively.
Main Takeaways:
- Fog computing processes data closer to its source
- Local processing enables real-time responses
- Key topics: components, applications, benefits
- Critical for future-ready computing systems
Understanding the Concept of Fog Computing
Smart devices can work faster and process data locally, without relying on distant computers. This local processing power comes from fog computing, an innovative approach that’s changing how our devices work.
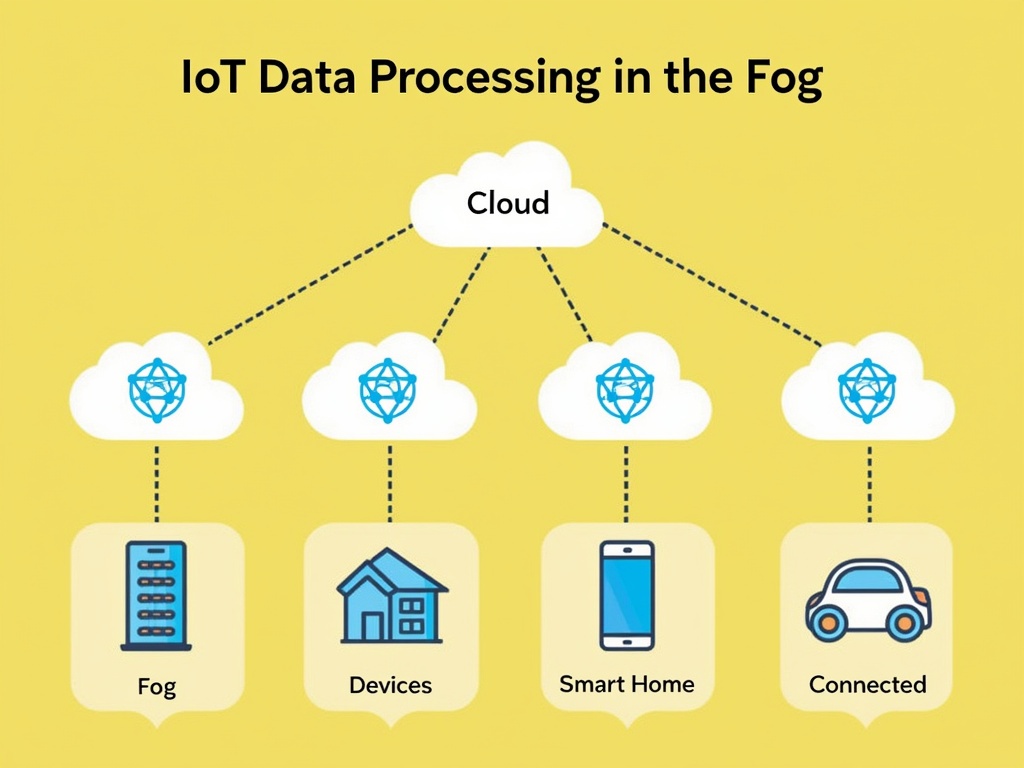
Fog computing moves cloud computing capabilities closer to your devices where data is created and used. Think of it as having a small data center right next to your devices instead of sending information to far-away servers.
The system works through fog nodes – specialized devices that act as local processors for nearby equipment. These nodes offer three main advantages:
They speed up processing time. Your device gets instant responses because data stays local instead of traveling to distant servers.
They reduce bandwidth usage. Processing data locally means less information needs to travel across networks, improving performance especially where internet access is limited.
Fog computing brings the cloud down to earth, allowing for faster, more efficient data processing at the network’s edge.
They protect your data better. Sensitive information stays local, reducing the risk of interception during transmission.
Fog computing connects smart homes, self-driving cars, and industrial sensors to create an efficient network. It serves as a bridge between cloud systems and IoT devices, keeping our connected world running smoothly.
This local processing approach leads to faster, more reliable, and more secure data handling for our connected devices.
Core Components of Fog Computing
Processing data near its source speeds up analysis and reduces delays. Here are the essential building blocks that power fog computing:
Edge Devices
Sensors, smartphones, and smart appliances work as data collectors at the front lines. These devices gather information and handle basic processing tasks right where the data starts.
A smart thermostat shows this in action – it reads your home’s temperature and adjusts your heating or cooling without asking a distant server what to do.
Fog Nodes
These local processors bridge the gap between edge devices and central systems. Fog nodes add computing power and storage exactly where needed.
Picture traffic lights with built-in fog nodes. They process data from nearby sensors to control traffic flow, sending only key updates to the main system.
Fog Servers
These powerful computers handle data from multiple fog nodes in an area. They have more processing muscle than individual nodes.
Factory fog servers collect sensor data from production lines to track efficiency and make quick adjustments that boost output.
Data Processors
Software running on fog nodes and servers makes decisions based on local data. These processors enable fast responses to changing conditions.
Retail stores use these processors to track customer patterns and inventory, automatically updating displays and restocking products as needed.
Fog computing connects cloud and edge computing, putting intelligence where data begins.
This network of components enables faster processing than traditional cloud systems. Applications that once seemed impractical now run smoothly in real-time.
| Component | Role |
|---|---|
| Edge Devices | Frontline data collectors that gather real-world information and perform basic data processing. |
| Fog Nodes | Intermediaries between edge devices and centralized computing resources, providing additional processing power and storage. |
| Fog Servers | Aggregate and process data from multiple fog nodes in a local area, offering substantial computing resources. |
| Data Processors | Specialized software components that handle analysis and decision-making based on collected data. |
Benefits of Fog Computing

Fog computing brings computation closer to data sources, addressing key challenges in modern data processing. This approach offers practical benefits for enterprises and IoT systems.
Reduced Latency
Fog computing processes data near its source, cutting transmission time between devices and servers. Smart traffic systems demonstrate this advantage – fog nodes process camera and sensor data locally, adjusting traffic lights instantly to prevent congestion. Traditional cloud systems can’t match this speed.
Better Performance
The distributed network of fog nodes improves system reliability and efficiency. Manufacturing plants use this capability for real-time machine monitoring. Local processing enables immediate failure prediction, reducing downtime and boosting productivity.
Stronger Security
Local data processing creates a more secure environment. Healthcare facilities benefit directly – patient monitoring devices process and encrypt sensitive data at the edge. This protects personal information even if central systems face compromise.
Lower Costs
While setup requires investment, fog computing reduces long-term expenses. Oil and gas operations showcase the savings – drilling sites process data locally, sending only essential information to the cloud. This cuts transmission costs and extends infrastructure life.
Fog computing complements cloud computing by bringing processing power closer to data creation points.
Dr. Tom Bradicich, VP and GM at Hewlett Packard Enterprise
Fog computing transforms data processing with faster responses, better security, and improved efficiency. As IoT devices multiply, this technology enables smarter, more responsive systems at the network edge.
Real-World Applications of Fog Computing
Fog computing processes data at the network edge, enabling faster responses and better performance across key industries. Here’s how this technology improves healthcare, urban infrastructure, and transportation.
Healthcare Applications
Fog computing enables instant medical data processing at the point of care. Wearable devices monitor vital signs and send immediate alerts to doctors. In hospitals, local fog nodes process medical images on-site, speeding up diagnoses.
GE Healthcare demonstrates this efficiency with their MRI machines – processing images at the edge cuts analysis time from 15 minutes to under 1 minute.
Smart City Solutions
Cities use fog computing to improve daily operations and public services. Traffic signals with fog nodes adjust automatically to traffic patterns, reducing congestion and travel times.
San Diego showcases these benefits through their smart lighting system, which has reduced energy usage by 60% while enhancing public safety.
Autonomous Vehicle Systems
Fog computing gives self-driving cars the speed they need for safe operation. Vehicles process sensor data locally for instant responses to road conditions. This local processing also enables direct vehicle-to-vehicle communication.
Tesla’s vehicles use edge computing to handle camera and sensor data, making real-time navigation decisions without depending on cloud connections.
Industry-Wide Benefits
- Faster response times for critical operations
- Better reliability with local processing
- Stronger data security and privacy
- Reduced network bandwidth usage
- Easy scaling for growing IoT networks
| Industry | Application | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Smart irrigation (SWAMP) | Better water use and distribution |
| Healthcare | eHealth systems | Faster diagnosis and secure monitoring |
| Smart Cities | Traffic and waste systems | Better traffic flow and city services |
| Education | Digital learning tools | Improved remote education delivery |
| Entertainment | Live streaming services | Smoother content delivery |
| Retail | Supply chain tracking | Real-time inventory management |
| Manufacturing | Smart factory systems | Reduced downtime, better efficiency |
As networks improve and devices advance, fog computing will become essential for connecting our digital world efficiently.
Challenges and Solutions in Fog Computing
Moving computing power to the network edge reduces latency and saves bandwidth, but this shift introduces several key challenges that need practical solutions.
Security Issues
Fog nodes face unique security risks due to their proximity to users and distributed nature. Studies show authentication and data privacy need particular attention in fog environments.
Key security measures include:
- Strong data encryption during transmission and storage
- Custom authentication systems for fog architectures
- Network-wide intrusion detection
Management Complexity
Managing resources across distributed fog networks presents unique challenges, especially with diverse device types.
Effective management solutions include:
- Standard fog computing frameworks
- Automated resource management tools
- Simple admin interfaces
Resource Limitations
Fog nodes have less computing power than cloud data centers, which can affect performance for demanding applications.
Smart solutions to maximize resources include:
- Efficient resource allocation systems
- Edge analytics to minimize data transfer
- Optimized applications for fog environments
Organizations can unlock fog computing’s benefits by tackling these challenges with targeted solutions. Ongoing technological advances will help address current limitations and strengthen fog computing’s role in modern data processing.
Conclusion: The Future of Fog Computing
Fog computing stands ready to transform modern data processing. The rapid expansion of IoT devices demands efficient, local data handling at the network edge.
Current challenges in standardization, security, and scalability require attention. Platforms like SmythOS offer solutions to these obstacles, making fog computing more accessible and reliable.
Organizations that adopt fog computing gain significant advantages: reduced latency, better analytics, and improved system reliability. Local data processing enables smarter, faster decisions where they matter most.
The combination of 5G networks and advancing AI technology amplifies fog computing’s impact. Smart cities and autonomous vehicles showcase its practical applications.
Modern data processing thrives on decentralization and adaptability. Organizations implementing fog computing today gain a competitive edge in this technological shift, positioning themselves to lead innovation across industries.
Last updated:
Disclaimer: The information presented in this article is for general informational purposes only and is provided as is. While we strive to keep the content up-to-date and accurate, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability of the information contained in this article.
Any reliance you place on such information is strictly at your own risk. We reserve the right to make additions, deletions, or modifications to the contents of this article at any time without prior notice.
In no event will we be liable for any loss or damage including without limitation, indirect or consequential loss or damage, or any loss or damage whatsoever arising from loss of data, profits, or any other loss not specified herein arising out of, or in connection with, the use of this article.
Despite our best efforts, this article may contain oversights, errors, or omissions. If you notice any inaccuracies or have concerns about the content, please report them through our content feedback form. Your input helps us maintain the quality and reliability of our information.