Imagine a city where cars drive themselves, traffic flows smoothly, and public services run like clockwork. This isn’t science fiction—it’s the power of autonomous agents in smart cities. These clever computer programs are transforming how our cities operate, making them safer, cleaner, and more efficient.
Autonomous agents act as invisible helpers. They manage traffic, run public services, and even make complex decisions. This article explores how these agents are shaping our urban future, the challenges they face, and their potential impact.
Explore the world of autonomous agents and discover how they’re making our cities smarter. From traffic lights that think for themselves to robots that keep our streets clean, these agents are enhancing city life for everyone.
Roles of Autonomous Agents in Smart City Infrastructure

Autonomous agents, powered by artificial intelligence, are transforming urban landscapes into efficient, responsive ecosystems. These digital sentinels optimize city operations in ways that were once the stuff of science fiction.
At the heart of this urban metamorphosis lies intelligent traffic management. Imagine a city where traffic lights adapt in real-time to vehicle flow, where congestion dissipates before it forms. This is happening now. Autonomous agents analyze vast streams of data from sensors and connected vehicles, making split-second decisions to keep traffic moving smoothly. The result? Shorter commutes, cleaner air, and relief from frustrated drivers.
But the benefits extend far beyond our roads. These agents are revolutionizing public services, making them more efficient and accessible. Consider a waste management system that optimizes collection routes based on real-time bin levels, or smart streetlights that dim when no one’s around, saving energy and reducing light pollution. These are fundamental shifts in how cities operate.
The infusion of AI Agents in smart cities heralds a new era of urban efficiency and sustainability. One notable use case is in traffic management, where autonomous AI Agents optimize traffic flow, reducing congestion and pollution.
Beam.ai
Public safety is also getting a high-tech upgrade. Autonomous agents monitor camera feeds, detecting potential incidents and alerting first responders faster than any human operator could. They can predict crime hotspots, allowing for more effective policing strategies. In emergencies, these agents coordinate response efforts, ensuring resources are deployed where they’re needed most.
Perhaps most exciting is how autonomous agents are enhancing the citizen experience. From chatbots that can answer city-related queries 24/7 to personalized public transit recommendations, these AI-powered assistants are making city living more intuitive and user-friendly. They’re breaking down barriers between residents and local government, fostering a sense of connection and engagement.
Of course, this technological leap doesn’t come without challenges. Privacy concerns, data security, and the need for robust accountability measures are all critical issues that cities must grapple with. But the potential benefits—reduced carbon emissions, improved quality of life, and more responsive urban services—make this a journey worth embarking on.
As we look to the future, it’s clear that autonomous agents will play an increasingly central role in shaping our urban environments. They’re not just making our cities smarter—they’re making them more livable, sustainable, and resilient. The smart city of tomorrow is being built today, one algorithm at a time.
Challenges Faced by Autonomous Agents in Smart Cities
Autonomous agents offer exciting possibilities for enhancing urban life, but their integration into smart cities presents significant hurdles. Three key challenges are ethical dilemmas, job displacement concerns, and technological limitations.
Ethical Challenges
The most complex challenge facing autonomous agents is ethics. As AI-powered systems take on more decision-making responsibilities, they encounter situations with moral implications. For example, a self-driving car may need to choose between two harmful outcomes in an unavoidable accident scenario. How do we program machines to make ethical choices that align with human values?
Algorithmic bias adds to this issue. If not carefully developed and monitored, autonomous systems may perpetuate or amplify existing societal biases related to race, gender, or socioeconomic status. Ensuring fairness and transparency in AI decision-making processes is crucial but incredibly difficult to achieve in practice.
We will reproduce all of our human faults in artificial form unless we strive right now to make sure that we don’t.
Attendee at the first meeting of the Partnership on AI
Job Displacement
As autonomous agents become more capable, concerns about widespread job losses loom large. While some argue that AI will create new types of jobs, many worry that the pace of displacement will outstrip job creation, leading to significant economic disruption. Industries from transportation to customer service could see major workforce shifts as autonomous systems take over routine tasks.
| Industry | Projected Job Displacement (%) |
|---|---|
| Clerical/Secretarial | 40% |
| Transportation | 25% |
| Customer Service | 65% |
| Manufacturing | 14% |
| Retail | 65% |
This challenge extends beyond simple unemployment numbers. There are deeper questions about human purpose and meaning in a world where machines handle an increasing share of work. How do we ensure that people can still find fulfillment and contribute meaningfully to society in an age of ubiquitous AI?
Technical Limitations
While AI has made remarkable strides, autonomous agents still face many technical limitations. These systems can struggle in complex, unpredictable environments—precisely the type of settings common in bustling urban centers. Issues like sensor reliability in adverse weather conditions, interpreting ambiguous human behaviors, and seamlessly integrating with existing infrastructure all present ongoing challenges.
Additionally, as autonomous systems become more prevalent, they become more attractive targets for malicious actors. Ensuring robust cybersecurity and protecting against potential hacks or manipulations of these agents is a critical technical challenge that must be addressed.
The Path Forward
Addressing these challenges requires a collaborative effort between technologists, policymakers, ethicists, and citizens. Developing clear ethical frameworks, investing in education and job transition programs, and continuing to advance the technical capabilities of AI systems are all crucial steps. By tackling these issues head-on, we can work towards realizing the potential benefits of autonomous agents while mitigating their risks.
As we navigate this complex landscape, maintaining a human-centered approach is key. Autonomous agents should augment and empower human decision-making rather than entirely replace it. By keeping this principle in mind, we can strive to create smart cities that harness the power of AI while preserving the values and agency of the people who call them home.
Future Trends in Autonomous Agents for Smart Cities
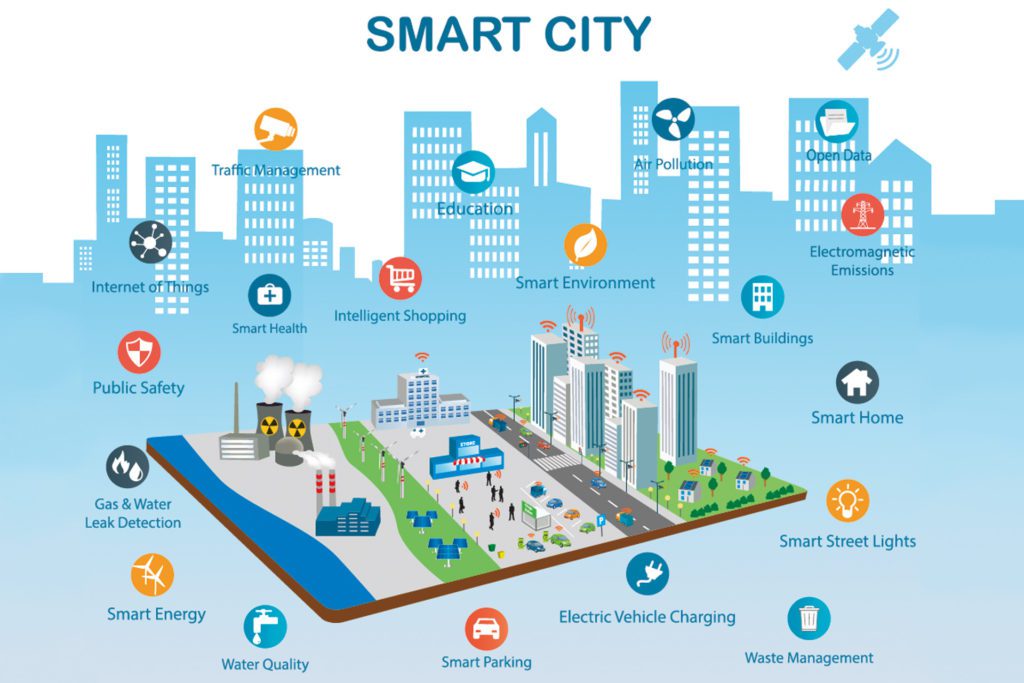
A vibrant smart city with IoT and modern infrastructure. – Via datasciencecentral.com
As artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities evolve, autonomous agents are set to transform urban environments. These intelligent systems will manage city infrastructures with minimal human intervention, leading to a new era of efficiency and sustainability.
One promising application is in utility network management. AI platforms can predict maintenance needs, optimize resource distribution, and respond to disruptions in real-time across power grids, water systems, and telecommunications networks. This level of intelligent automation could reduce waste and improve service reliability for millions of urban residents.
Transportation is another area ready for transformation. Self-driving vehicles communicating via 5G networks will form coordinated platoons, easing traffic congestion and enhancing road safety. AI-powered traffic management systems will dynamically adjust signals and routes to keep people and goods flowing smoothly through busy city streets.
Environmental sustainability will benefit greatly as well. Smart waste management systems will optimize collection routes and sorting processes. Autonomous drones and sensors will monitor air and water quality, enabling rapid responses to pollution events. Buildings will become more energy-efficient through AI-controlled systems that precisely manage heating, cooling, and lighting.
Realizing this potential requires careful planning and investment in smart infrastructure. Cities must lay the groundwork by deploying sensors, upgrading communication networks, and creating policies that foster innovation while protecting privacy and security. The transition won’t happen overnight, but the foundations are being laid today for the autonomous, sustainable cities of tomorrow.
As these technologies mature, we may see entire urban districts managed almost entirely by interconnected AI agents. While this prospect might seem daunting to some, it holds immense potential to enhance quality of life, reduce environmental impact, and create more livable cities for all. The future of smart cities is autonomous, and it’s closer than we think.
How SmythOS Enhances Autonomous Agents in Smart Cities
Robots and holograms in a high-tech workspace. – Via smythos.com
SmythOS is transforming the development and deployment of autonomous agents in smart cities. By offering a comprehensive platform with advanced features, it’s paving the way for more intelligent and efficient urban environments. Let’s explore how SmythOS is making this possible.
At the heart of SmythOS is its intuitive visual workflow builder. This tool allows developers to craft sophisticated AI agents without complex code. Imagine creating an autonomous traffic management system by simply dragging and dropping components – that’s the power SmythOS puts in your hands. This visual approach speeds up development and opens doors for urban planners and city officials who may lack deep coding skills but possess invaluable domain knowledge.
SmythOS isn’t just about simplicity; it’s about versatility too. The platform’s multi-model support is a standout feature for smart city applications. Different urban challenges require different AI approaches, and SmythOS delivers. Whether you’re optimizing energy grids with reinforcement learning or predicting maintenance needs with deep learning, SmythOS provides the flexibility to choose the right tool for each job.
Security is paramount in urban infrastructure, and SmythOS doesn’t disappoint. Its enterprise-grade security measures ensure that sensitive city data and critical systems remain protected. This robust security framework allows cities to innovate with confidence, knowing their AI agents are shielded from potential threats.
SmythOS also excels in its ability to integrate with existing urban systems. Smart cities are complex ecosystems, and SmythOS acts as the connective tissue, allowing autonomous agents to communicate seamlessly with various data sources and APIs. This interoperability is crucial for creating a truly smart city where information flows freely between systems.
SmythOS isn’t just another development platform – it’s a catalyst for urban innovation. It’s empowering cities to turn AI visions into reality, faster and more cost-effectively than ever before.
Alexander De Ridder, Co-Founder and CTO of SmythOS
The real-world impact of SmythOS in smart cities is already evident. From optimizing public transportation routes in real-time to managing energy consumption across city blocks, SmythOS-built agents are driving efficiency and improving quality of life for urban dwellers.
As we look to the future, the potential of SmythOS in smart city development is boundless. Its ability to democratize AI development while providing robust, scalable solutions positions it as a key player in shaping the cities of tomorrow. With SmythOS, the dream of truly intelligent urban environments is not just possible – it’s happening right now.
Conclusion: Embracing Autonomous Agents for Smarter Cities
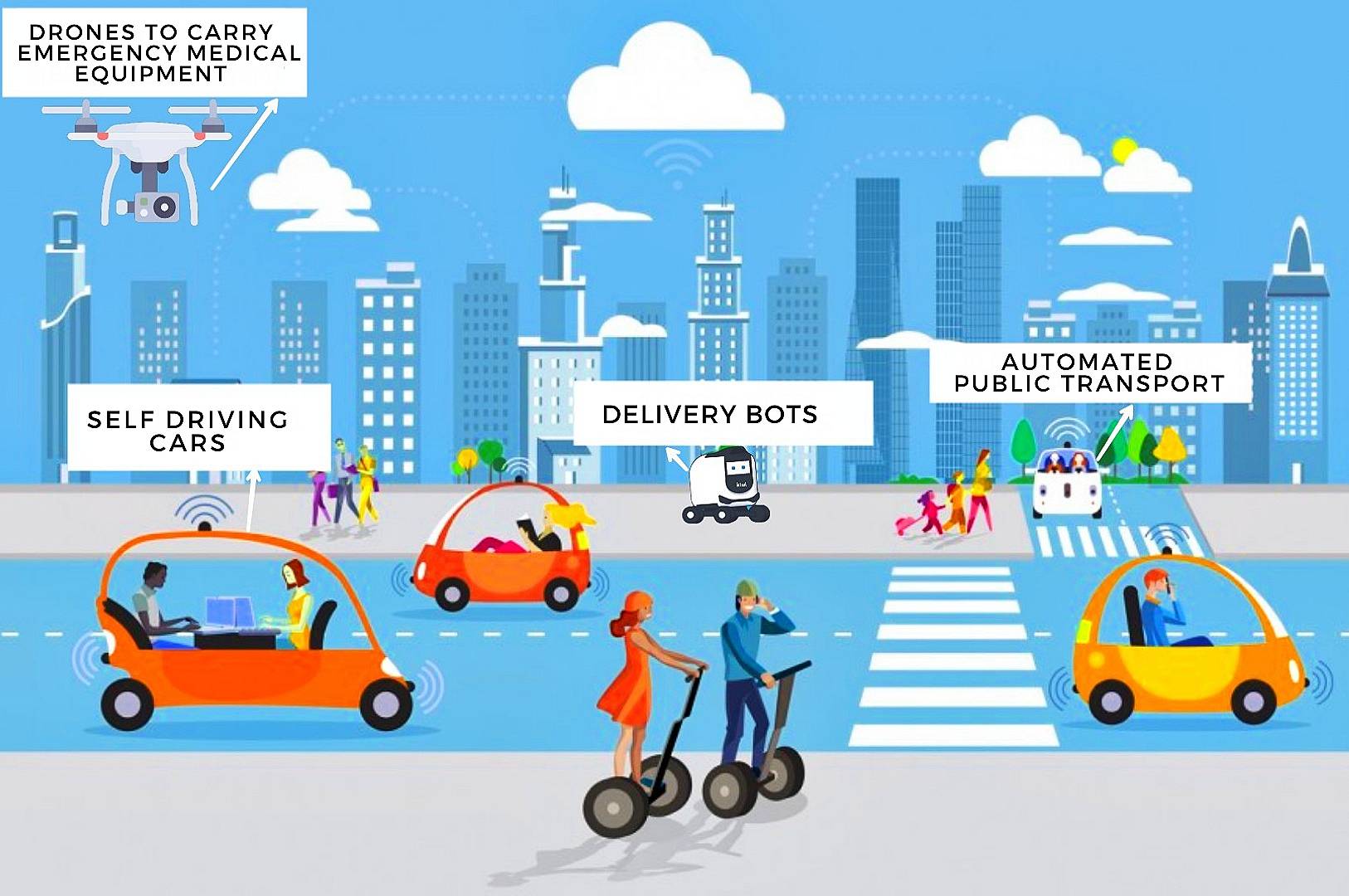
Showcasing advanced urban mobility solutions. – Via technology-innovators.com
Autonomous agents are set to transform urban landscapes, bringing unprecedented efficiency, safety, and sustainability to smart cities. These AI-powered entities promise a future where urban challenges are met with intelligent, adaptive solutions. From optimizing traffic flow and reducing congestion to enhancing public services and improving resource management, autonomous agents hold the potential to revolutionize city life.
By leveraging real-time data analysis and decision-making capabilities, these digital assistants enable municipal leaders to make informed choices that benefit both residents and the environment. However, integrating these technologies demands careful attention to ethical considerations, data privacy, and the necessity of human oversight. Balancing innovation with responsible implementation is essential to creating safe, equitable cities.
Platforms like SmythOS provide a robust framework for developing and deploying autonomous agents, empowering cities to harness AI benefits while maintaining control and transparency. With its intuitive interface and powerful capabilities, SmythOS is an ideal tool for urban planners, policymakers, and technologists aiming to build smarter, more responsive cities.
The question isn’t whether to embrace autonomous agents, but how quickly and effectively we can integrate them into our city systems. Doing so opens the door to efficient resource allocation, an improved quality of life for residents, and a more sustainable future. The path to smarter cities is clear, paved with the potential of autonomous agents. As we move forward, let’s approach this transformation with optimism, creativity, and a commitment to building urban environments that serve all inhabitants. The future of our cities is autonomous—and it’s brighter than ever before.
